SCM in Logistics: Key Differences Between Logistics and Supply Chain
The freight world often uses two standard terms: Supply Chain Management (SCM) and Logistics Management (LM). These terms are often used interchangeably, and not many people know the difference between them.
Logistics management is a small portion of Supply Chain Management that combines the flow of goods, services, information, and capital right from raw material to its final consumer. Whereas, supply chain management is much broader and starts right from the product’s source to delivering it to the consumers. Each of these has different functions and processes and is different in many aspects.
Before we start picking out the differences, let’s get a brief overview of both supply chain and logistics.
What is Supply Chain Management?
According to Supply Chain Logistics Management, a book by professors of Michigan State University, Supply Chain Management or SCM involves collaboration between firms to connect suppliers, customers, and other partners to boost efficiency and produce value for the end consumer.
In a broader sense, Supply Chain Management is a three-part process. It starts with sourcing the raw materials for the product, goes through manufacturing processes, and finally gets dispatched to the end buyer. The process is complicated due to many factors and needs intense planning and strategies.
Check out our Freight Knowledge Base for resources and FAQs on freight forwarding for logistics and supply chain professionals.
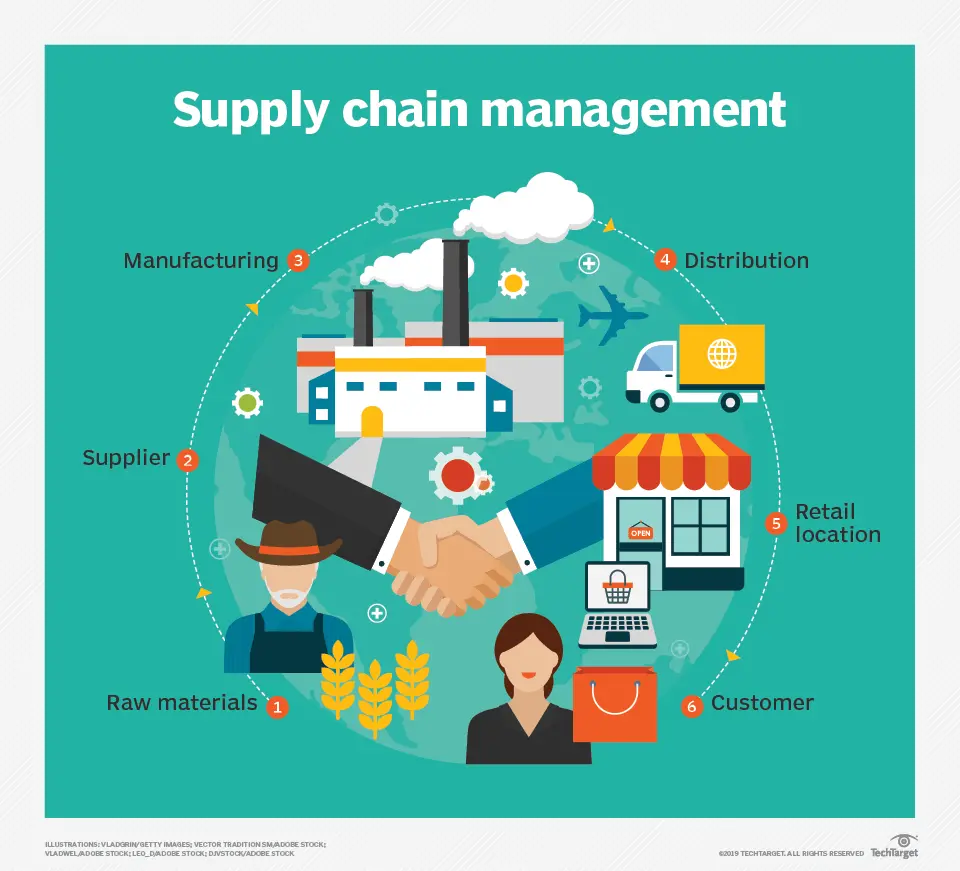
Businesses and companies go out of their way to optimize their supply chain management to incur fewer losses and enhance the business’s productivity. Supply Chain Managers are the personnel who take care of your supply chain logistics and devise various strategies to optimize each part of this process.
What is Logistics Management? Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Logistics is a part of SCM, focusing on the movement, storage, and flow of goods within the supply chain. Its main goal is to get products from one place to another in the most efficient way. This includes transporting raw materials to a factory, moving finished products to warehouses, and delivering goods to customers.
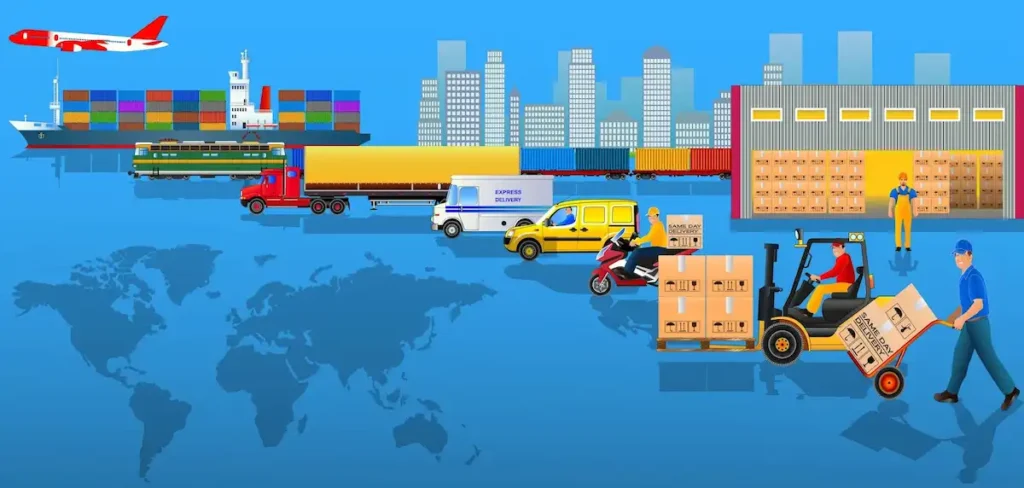

Logistics includes several areas:
- Transportation: Moving goods by road, rail, air, or sea.
- Warehousing: Storing products before they are shipped.
- Inventory Management: Keeping track of stock levels.
- Order Fulfillment: Processing and delivering customer orders.
In simple terms, logistics is about making sure that each step runs smoothly so that products reach their destination on time. For instance, a company selling electronics needs reliable logistics to deliver parts to its factory and then ship finished products to customers or stores. Logistics also covers managing stock levels so that items aren’t overstocked or understocked, ensuring a balance that meets demand without excess.
Differences Between Logistics and Supply Chain Management
SCM and logistics overlap but aren’t the same. Here are the key differences:
- Scope: Logistics is one part of SCM. SCM covers the entire journey, while logistics focuses on moving and storing goods within this process.
- Goals: Logistics focuses on getting products where they need to go, on time, and in good condition. SCM’s goal is broader: to make the entire chain efficient and cost-effective, from sourcing materials to delivering the product.
- Focus: Logistics looks at the operational details; getting goods from one location to another. SCM focuses on strategy and coordinating all partners in the chain, from suppliers to retailers.
- Process: Logistics involves transportation, warehousing, and stock control. SCM includes these but adds planning, sourcing, and production.
Common SCM and Logistics Challenges and Solutions
Supply chain management and logistics face various challenges that can disrupt operations if not properly addressed. Here are some common issues and effective solutions to overcome them:
Demand Fluctuations: Sudden changes in demand can lead to stockouts or excess inventory.
Solution: Implement demand forecasting tools to predict customer needs accurately and plan inventory levels accordingly.
Supply Chain Disruptions: Unforeseen events like natural disasters or political issues can halt production or delay shipments.
Solution: Develop a resilient supply chain with multiple suppliers and diversified routes to minimize disruption risks. You can utilize a real-time visibility tool to find alternative routes.
Inventory Management: Balancing stock levels without overstocking or understocking is complex.
Solution: Use inventory management systems that offer real-time tracking to maintain optimal stock levels and avoid inefficiencies.
High Transportation Costs: Rising fuel prices and route inefficiencies drive up transportation expenses.
Solution: Optimize routes using AI-driven tools, and consider a mix of transportation modes to reduce costs.
By addressing these challenges, businesses can improve SCM and logistics efficiency, which translates into more reliable product delivery and better customer satisfaction.
GoComet has a solution for all these challenges, find out more!
The Role of SCM in Logistics Operations
SCM plays a critical role in making logistics more efficient. By organizing the entire supply chain, SCM ensures that logistics operations run smoothly. For example, if a company knows its production schedule, it can plan logistics to ensure the timely delivery of materials and products. SCM also helps logistics teams adapt to changes in demand and avoid delays.
SCM in logistics enables better communication across all levels of the supply chain. This includes suppliers, manufacturers, and customers. Let’s say a company faces a sudden demand increase; SCM allows the logistics team to respond quickly, adjust delivery schedules, or even find alternative routes if needed. SCM also promotes real-time tracking of goods, so logistics teams know exactly where products are at any moment, which helps avoid delays.
The Impact of Technology on SCM in Logistics
Technology has transformed both SCM and logistics, making them faster and more reliable. Today, tools like AI, IoT (Internet of Things), and data analytics have made SCM in logistics more efficient and adaptable.
- Real-Time Tracking: Many companies use GPS and IoT sensors to track goods at every stage. This allows them to monitor deliveries in real time and respond to delays or issues immediately.
- Data Analytics: Data is powerful in SCM. With analytics, companies can predict demand, manage stock, and plan better. This also helps logistics teams prepare for busy periods and avoid bottlenecks.
- Automation: From robots in warehouses to automated vehicles for transport, automation reduces manual work and speeds up operations. Automated systems improve accuracy and lower the chances of human error.
- AI and Machine Learning: AI helps SCM teams optimize delivery routes, manage stock levels, and even predict potential supply chain issues. This allows logistics to be proactive rather than reactive.
For example, a retailer can use data from past sales to predict future demand, so logistics teams know when to increase deliveries to certain stores. Automation in warehouses means that products move faster, which shortens delivery times and improves customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between SCM and logistics helps businesses improve efficiency and deliver value to customers. SCM is the strategic approach that plans and coordinates the entire product journey. Logistics is the operational part, focusing on moving and storing goods within the supply chain. Together, SCM and logistics ensure products reach customers quickly, reliably, and cost-effectively.
FAQs
1. Is SCM the same as logistics?
No, SCM is broader. It manages the entire journey of a product, from sourcing to delivery. Logistics focuses on transportation and storage within this journey.
2. How does SCM benefit logistics?
SCM organizes the supply chain, making logistics more efficient. It ensures timely deliveries, better stock control, and quick adaptation to demand changes.
3. What role does technology play in SCM in logistics?
Technology improves Supply Chain Management and logistics by providing real-time tracking, data analytics, and automation. These tools make processes faster, more accurate, and adaptable.
4. Why is SCM important for logistics operations?
SCM coordinates all parts of the supply chain, helping logistics teams work smoothly with suppliers, manufacturers, and customers. It also allows quick responses to delays or demand spikes.
5. How are SCM and logistics different in terms of goals?
Logistics aims to transport and store goods efficiently. SCM’s goal is broader: to manage the entire supply chain and maximize efficiency across all stages.
Check out our tool, GoComet Freight Index, to benchmark your freight rates with industry standards!






